RHCSA Exam Environment: What to Expect on Exam Day
Published On: 11 February 2025
Objective
The RHCSA exam is difficult, but knowing what to expect on the day of the exam helps relieve stress. This guide covers everything you need to know about the testing environment, including remote setup and access to the exam via USB boot, as well as helpful tips and strategies for passing the RHCSA exam.
RHCSA Exam Overview
The RHCSA exam (EX200) is a practical, performance-oriented assessment designed to evaluate your real-world skills in Linux system administration using Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL). Unlike conventional multiple-choice tests, the RHCSA exam requires you to showcase your ability to execute essential system administration tasks directly on an active system. For more detailed information on exam objectives, check out our blog “RHCSA Exam Objectives”.
About Exam :
-
Language - English (en)
-
Duration - 3 hours
-
Format - Hands-on practical assignments
-
Number of Tasks - Around 20 performance-based tasks
-
Fee - $500
-
Validity - 3 years
-
Passing Score: 210 / 300
-
Scoring: Based on task completion and best practice adherence.
-
Scores were reported within 3 US business days.
-
Difficulty level: Easy but requires a solid understanding of system administration basics
Note:
-
The exam provides no internet access, so you'll use your knowledge and available resources.
Exam Type:
The exam is available in both online and offline modes as per your preference.
-
Offline(Test Center): A nearby test center will be assigned to you.You'll need to verify your identity to gain access, and the exam will be pre-configured at the center.
-
Remote (USB Boot): You can take the exam remotely from home, but you'll need to set it up using a USB boot.
Taking the RHCSA Exam Remotely (USB Boot)
For remotely taking the RHCSA exam, you must boot up into a secure USB image provided by Red Hat. Here’s what you need to know to prepare:
1. System Requirements
Before the exam begins, make sure your system meets the following requirements:
-
Processor: Intel i5 or AMD Ryzen 5 (or better)
-
RAM: At least 8GB (16GB recommended for smooth performance)
-
Storage: At least 20GB of free space
-
USB Drive: Minimum 8GB capacity for bootable image
-
Internet Speed: Minimum 10 Mbps (wired connection recommended)
-
External Webcam: Required for remote proctoring
-
Dual Monitors: Not allowed (Single monitor only)
-
Secure BIOS Settings: Some systems may require Secure Boot to be disabled for USB booting
2. Downloading & Preparing the Remote Exam USB
-
Red Hat will provide you a secure bootable USB image that you need to download and install on your USB drive.
-
You may use Fedora Media Writer or the dd command, for instance, to burn the image onto your USB.
-
Restart your system and boot from the USB (adjust BIOS boot order if needed).
Troubleshooting Boot Issues:
-
Ensure Secure Boot is disabled in BIOS.
-
Use a different USB port if your system does not recognize the boot drive.
-
If the USB does not boot, re-burn the image using Fedora Media Writer or Balena Etcher.
3. Logging into the Exam Environment
-
After booting from the USB, the system will load into a locked-down exam environment that restricts access to external resources.
-
Please log in using your Red Hat credentials.
-
A proctoring session will be conducted before the exam starts to verify your identity and check your room setup through your webcam.
-
Once your identification has been verified, the exam will begin, and you will enter the virtualized RHCSA lab environment, which has been configured so that you can complete the tasks given to you.
4. Navigating the Exam Interface
Once you begin the RHCSA exam, you'll enter a secured exam environment where you'll work with several virtual machines (VMs). This system is structured to replicate actual administrative tasks, and your capability to navigate this setup effectively is crucial for success. Here’s what you’ll see:
-
Multiple Virtual Machines (VMs):
-
The exam setup will include multiple virtual machines (usually 2 to 3) that simulate various Linux systems you will be working with.
-
Each VM may serve a distinct function (such as web server or database server), and you’ll need to configure and manage them according to the specified tasks.
-
You might have to switch between VMs, particularly when tasks necessitate collaboration between different systems, like configuring a web server and setting up networking.
-
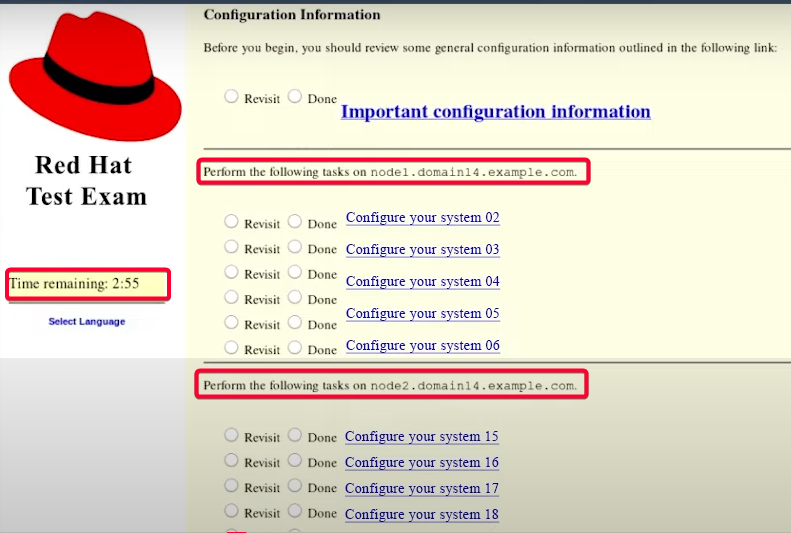
Structured Task Layout:
-
Tasks will be presented on the screen in an organized and easy-to-understand layout.
-
You can follow the tasks one step at a time and will need to utilize the available resources to complete them.
-
The interface will likely include some form of task descriptions and clear instructions to help you know exactly what needs to be done.
-
Terminal Access:
-
The terminal window will be your main interface for completing tasks.
-
Most of your time will be spent in the terminal, where you'll issue commands to manage users, configure networking, set up services, and carry out various administrative tasks.
-
You will have access to a bash shell or a similar terminal interface to execute these commands, allowing for direct interaction with the system
-
Graphical tools may be available in certain situations, but generally, you’ll rely on the command line. Tasks will guide you on when a GUI is needed.
-
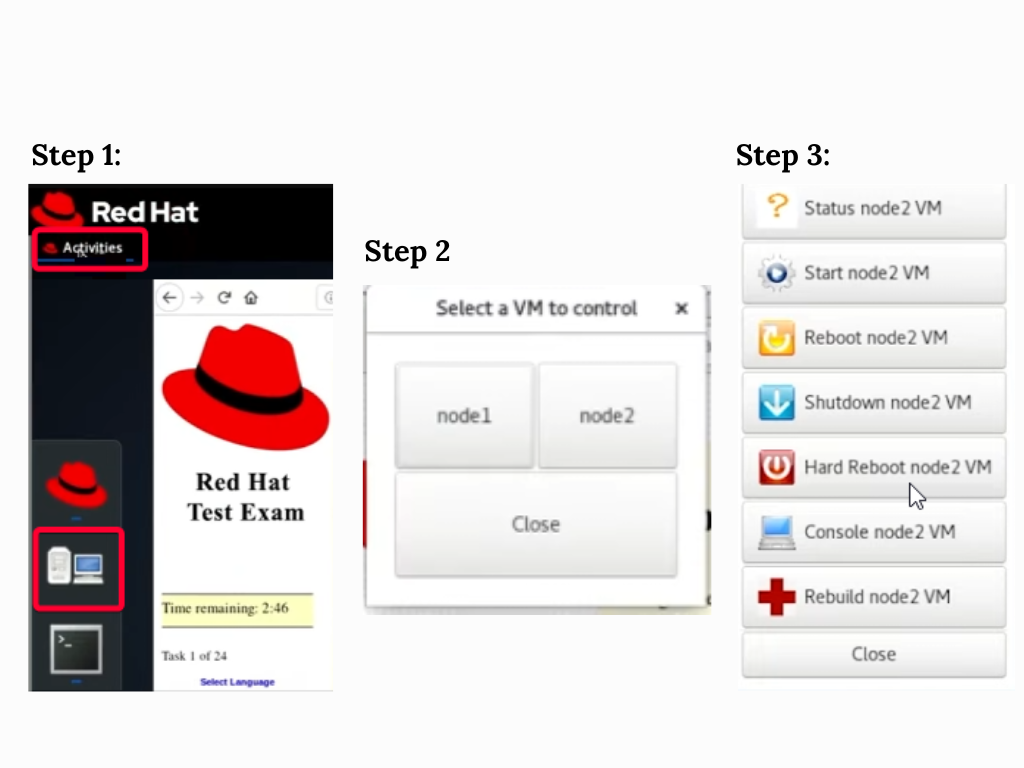
Switching Between VMs:
-
You can effortlessly switch between VMs to carry out different tasks.
-
For instance, you may need to configure user accounts on one machine while setting up a firewall on another.
-
Be prepared to handle multiple windows or terminal sessions simultaneously.
-
Shutting Down and Rebuilding a VM
-
At times, you may need to shut down or rebuild a virtual machine.
-
Shutting down is done through the VM control panel.
-
Rebuilding a VM erases and resets it, which can be helpful if a configuration goes wrong otherwise it is not recommended.
-
To rebuild a VM:
-
Click the “Rebuild” button.
-
Confirm the action by typing “CONFIRM” in all caps.
-
Wait for the system to reset.
-
Using Shortcuts:
-
While common shortcuts like Ctrl + C, Ctrl + X, or Ctrl + V may work, they are not recommended as they can cause the terminal or exam browser to freeze. Instead, use your mouse for copy-paste actions.
-
To copy-paste:
-
Highlight text, right-click, and select “Copy.”
-
Right-click in the terminal and select “Paste.”
-
Proctoring and Monitoring:
-
Your exam session will be monitored remotely via a webcam.
-
A proctor will confirm your identity and inspect your surroundings before you begin.
-
Once the proctoring process is complete, the tasks will be available for you to begin.
-
Taking a Break
-
If you need a break, click the chat icon and select the break option.
-
Your proctor will be notified, and your exam timer will continue running.
-
Avoid using any external devices, as your exam is being recorded, and unauthorized actions may result in forfeiture.
Example RHCSA Exam Question
Here’s a sample question that illustrates the type of task you might be asked to perform on the RHCSA exam:
Task: You need to configure a new user named devops with the following specifications:
-
Set the password to Redhat123
-
Assign the user to the developers group
-
Ensure the user’s home directory is located at /home/devops
-
Set up a cron job to run /usr/local/bin/backup.sh every day at 2 AM
Expected Steps to Complete This Task
-
Create the user with the required home directory and group:
-
sudo useradd -m -G developers devops -
The -m flag ensures the home directory is created.
-
Set the user’s password:
-
echo 'Redhat123' | sudo passwd --stdin devops -
Verify the user’s home directory:
-
ls -ld /home/devops -
Add a cron job for the user to run the backup script at 2 AM daily:
-
sudo crontab -u devops -e -
Add the following line to the cron configuration:
-
0 2 * * * /usr/local/bin/backup.sh
5. How to Buy the RHCSA Exam
To register for the RHCSA (EX200) exam, purchase the exam from Red Hat's official website.
-
Visit the Red Hat Certification Website:
-
Go to the Red Hat Certification page to begin the registration process.
-
Create or Log into Your Red Hat Account:
-
You need a Red Hat account to buy the exam. If you don't have one, create an account by entering your information.
-
Select the RHCSA Exam (EX200):
-
Navigate to the section for selecting certification exams and select the RHCSA (EX200) exam.
-
Choose Your Exam Delivery Method:
-
You may take a remotely proctored online exam or an in-person test at a nearby testing location, depending on what's available in your area.
-
If you choose the remote exam option, ensure that your computer meets the technical requirements previously outlined.
-
Pay for the Exam:
-
The RHCSA exam costs $500 USD.
-
Once you’ve selected your exam and delivery method, proceed to payment.
-
Red Hat offers various payment methods, including credit cards and invoicing for certain regions.
-
Confirm Your Registration:
-
Once your purchase is complete, an email will be sent to you containing information about your exam schedule, access instructions, and other details.
-
Prepare for the Exam:
-
After registration, you can begin your preparation with the official Red Hat documentation, practice in your lab setup, and use online training materials.
Recommended Video for RHCSA Exam Environment
For a more comprehensive and visual walkthrough, check out this video guide:
Tips and Strategies for Success in the RHCSA Exam
1. Simulate the RHCSA Environment with Virtual Labs
-
Create a RHEL lab environment utilizing VirtualBox, KVM, or other virtualization software. Working in a simulated environment will allow you to become familiar with the tasks and the user interface.
-
Focus on mastering the command line since many tasks will be performed there.
2. Effective Time Management
-
The RHCSA exam is time-sensitive. While each task varies in difficulty, it’s important to manage your time effectively:
-
Start with easier tasks to build confidence and save more time for complex ones.
-
Don’t dwell too long on one task. If you’re stuck, move on and come back to it later if time allows.
3. Familiarize Yourself with Common Commands
-
Knowing common Linux commands and their syntax is crucial.
-
Make sure you’re familiar with commands for user management (useradd, passwd, etc.), package installation (yum), file manipulation (cp, mv, rm), and networking tools (ip, hostname, ss).
-
Understand key system administration tools like systemd, journalctl, and firewalld.
4. Leverage the Built-in Help Resources
-
Man pages and command-line help are available throughout the exam.
-
Use them effectively to quickly recall syntax or command options.
-
Example: man ls or ls --help
5.Know How to Troubleshoot System Issues
-
Troubleshooting is a key part of system administration.
-
Become comfortable looking through system logs: journalctl, dmesg, and the logs in /var/log/.
-
Understanding basic system diagnostics and troubleshooting will help you solve problems efficiently if they arise during the exam.
6. Prepare for Common Configuration Tasks
-
Many RHCSA tasks involve configuring services like SSH, NFS, and managing file systems.
-
Prepare these configurations in advance to guarantee that you can execute them swiftly and with confidence.
If you want to familiarize yourself with the RHCSA exam subjects and the testing environment prior to the actual exam, RHCSA Guru is the ideal resource. We provide comprehensive labs for each exam topic to enhance your skills. Moreover, our practice tests are structured to simulate the actual exam closely so that you can evaluate your level of preparation and enhance your confidence prior to the real exam.
Conclusion
The RHCSA exam is a complete evaluation of practical skills in Linux system administration. Success on the exam requires prior knowledge of the exam environment, preparation, and regular practice. During the exam, stay focused, manage your time well, and make the best use of whatever resources are provided.Best of luck with your RHCSA exam preparation! Remember to keep practicing, stay composed, and tackle the exam with confidence.